|
(c) 2012 - 2017 * updated MAR 2020 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
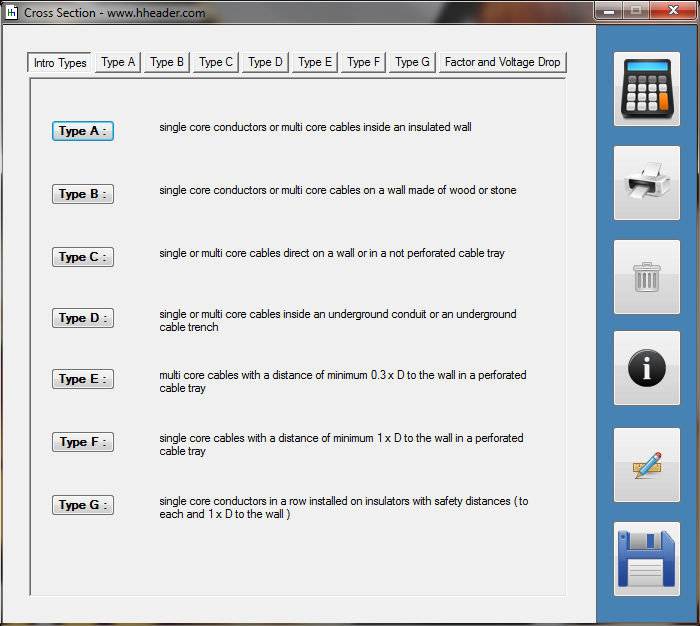
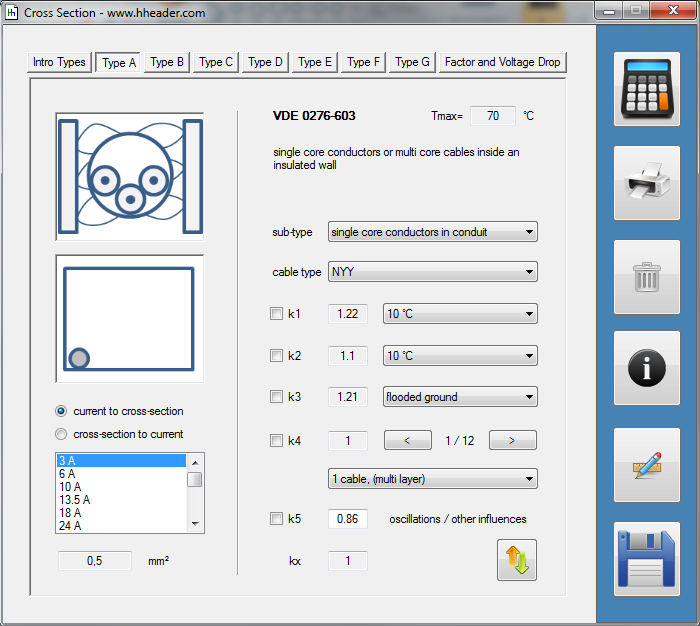
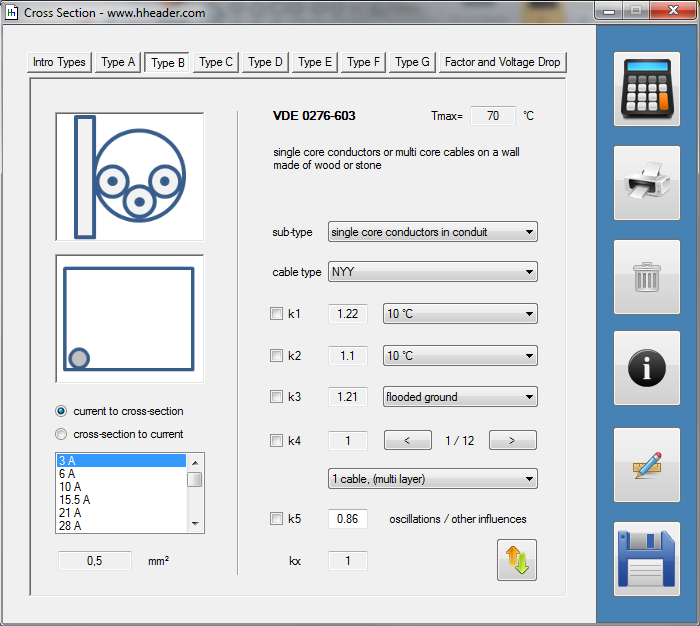
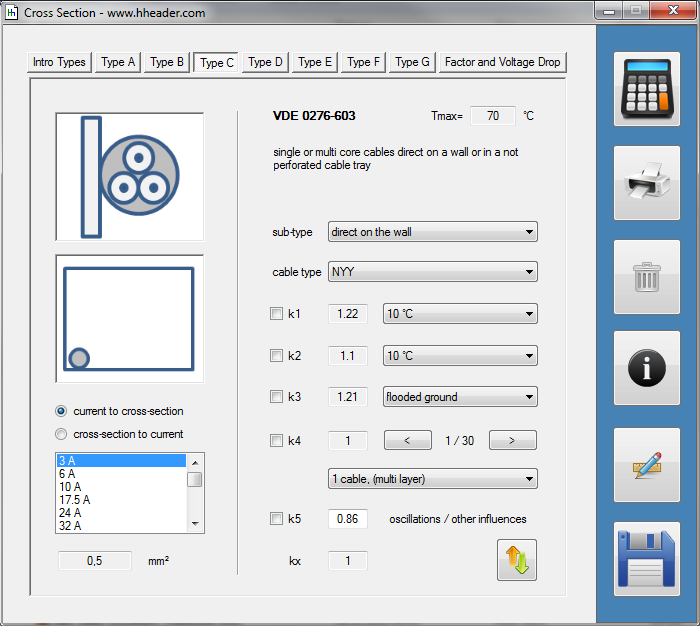
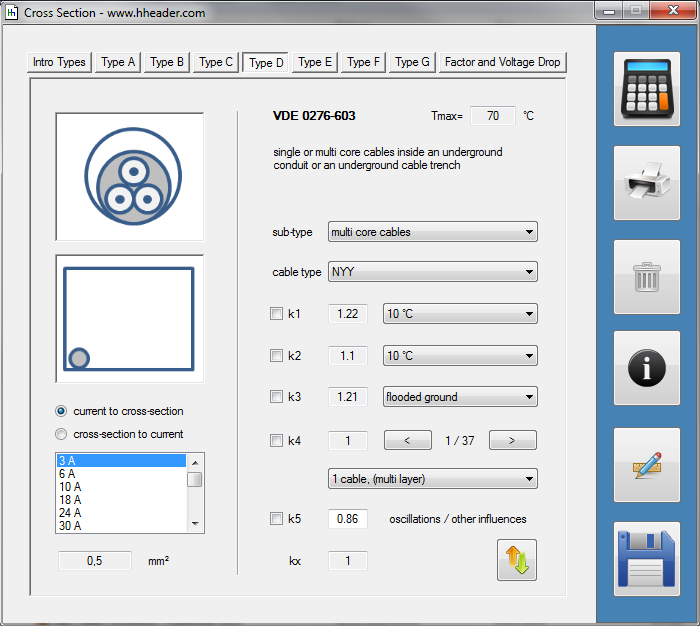
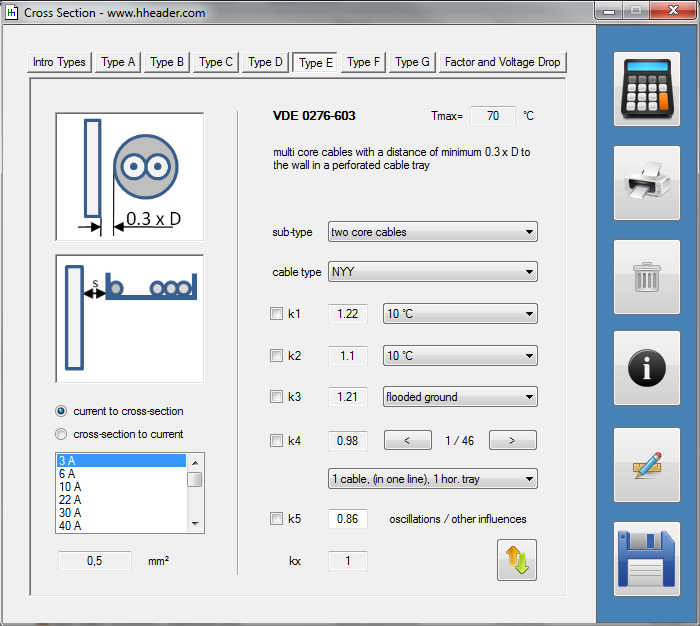
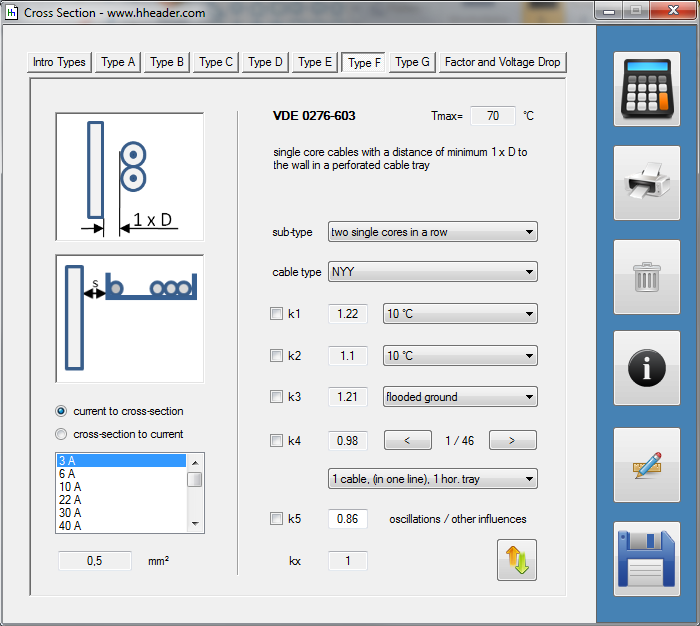
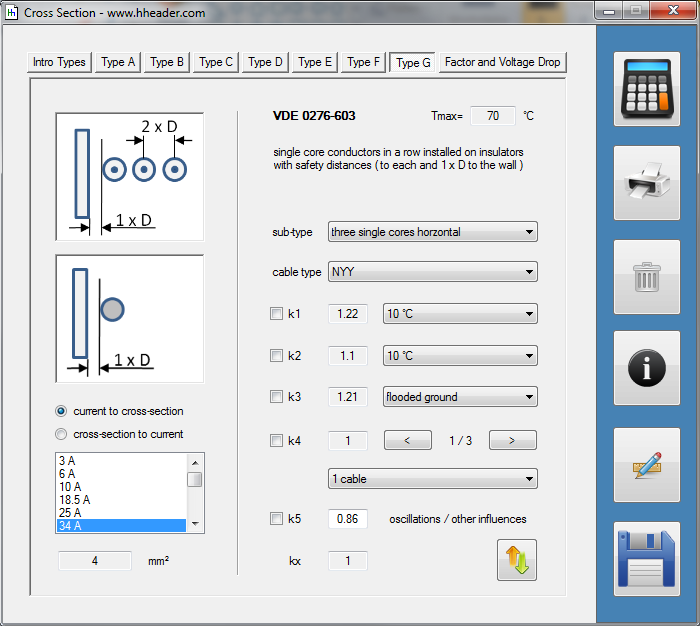
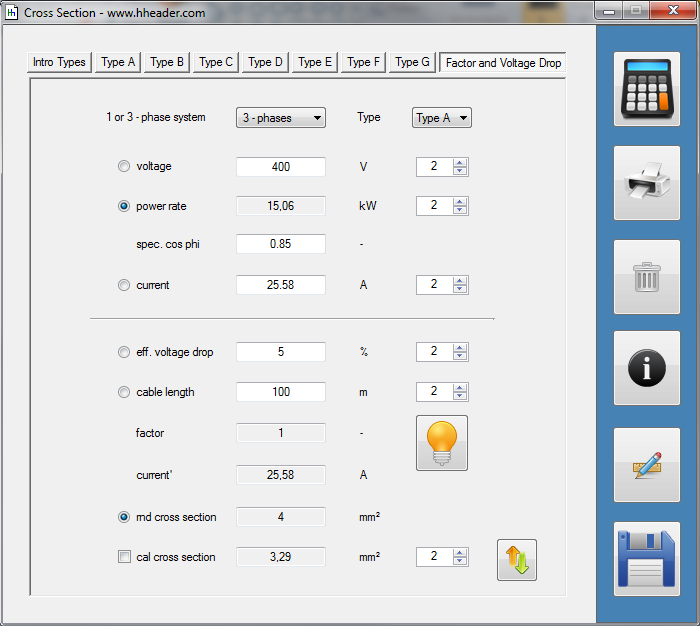
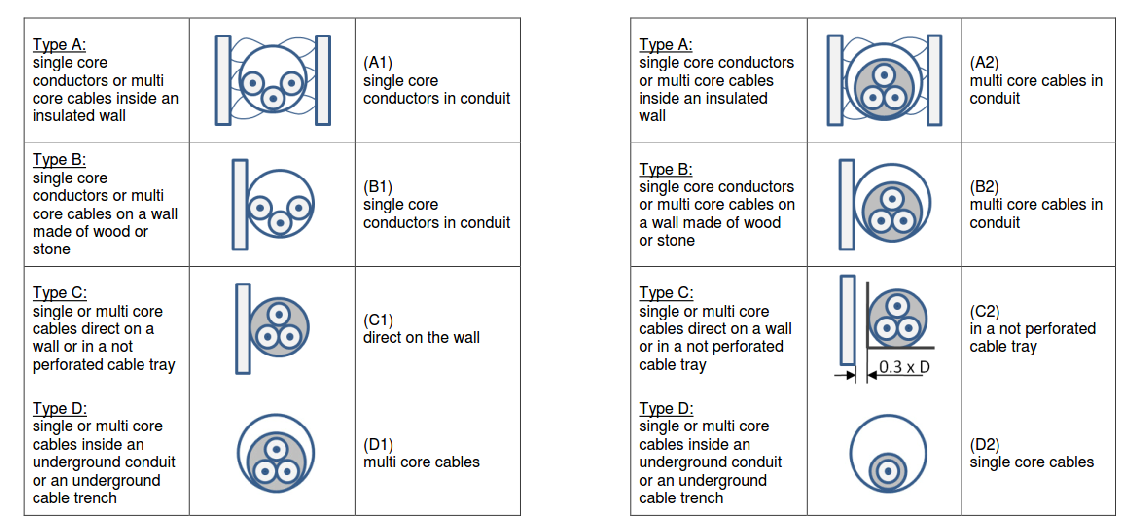
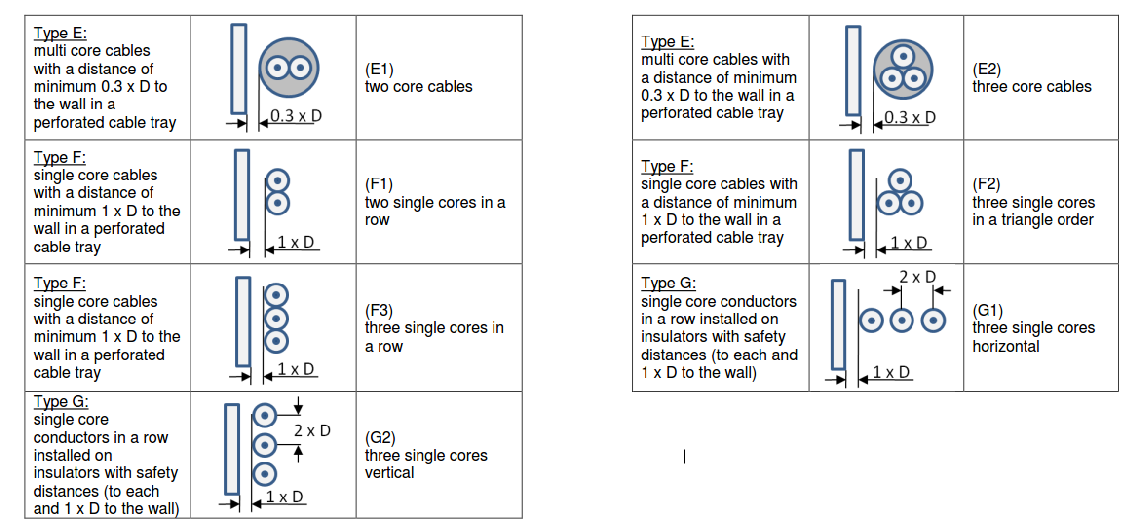
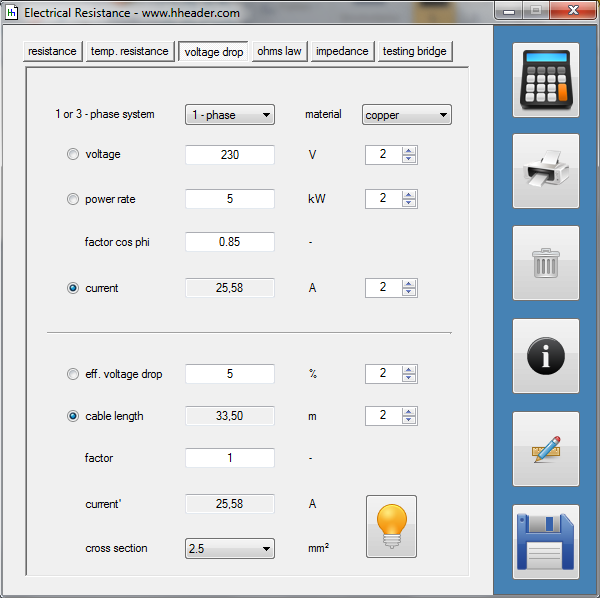
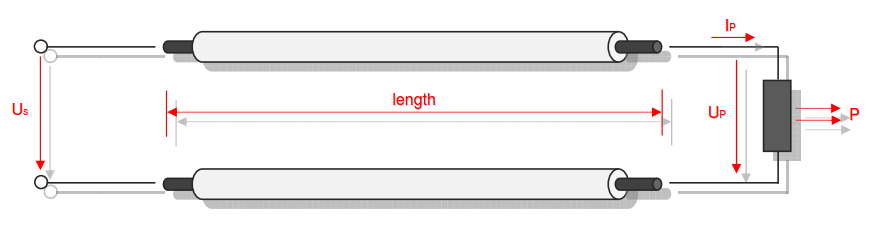
Category 5 - Electrics: Cross SectionFor the electrical power supply of a motor, an engine, a plant or in general any electrical consumer a proper cable with a proper cross section has to be selected due to the installation and operation circumstances. Regarding this different factors, design criteria and circumstances have to be taken into consideration.The following points are relevant: the routing, the amount of cores, the cable type, the distances, the ambient circumstances, the cable arrangement, further influences (oscillation effects etc.) and the voltage drop. For the voltage drop the cable length, the cross section, the core material and the current are significant factors. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
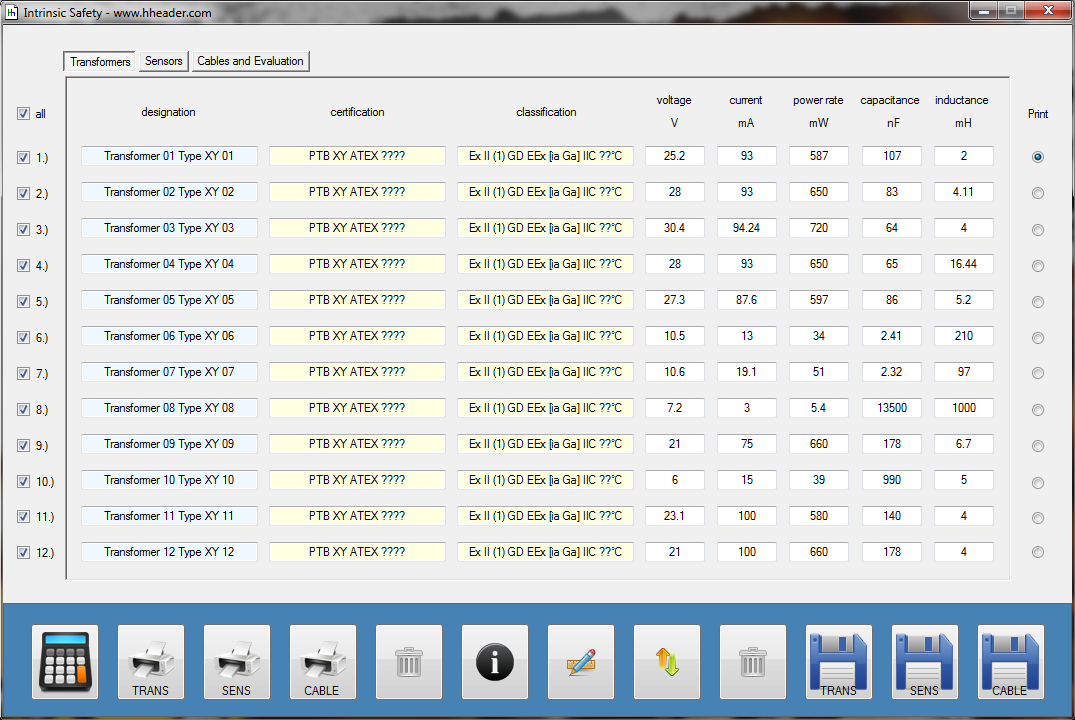
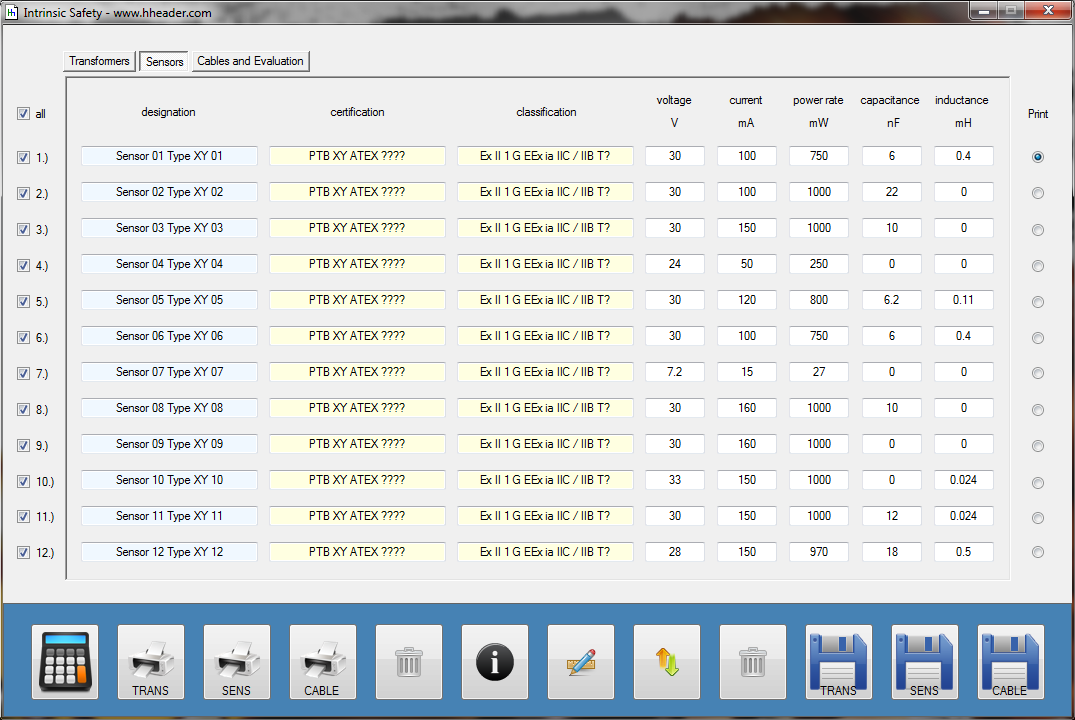
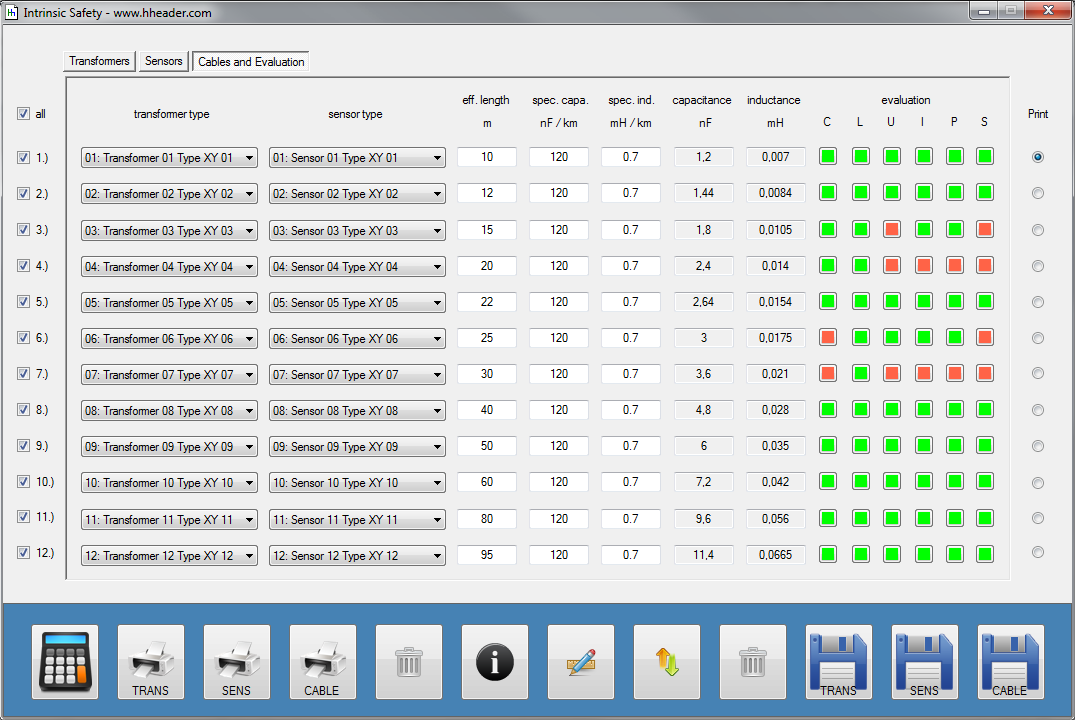
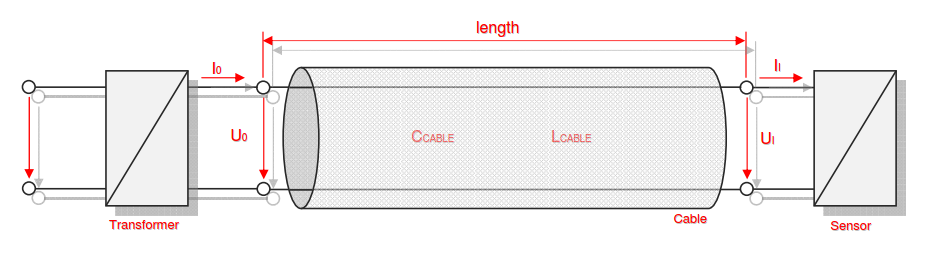
Category 5 - Electrics: Intrinsic SafetyIf there is a probability for the occurrence of an explosive atmosphere on site, special installation equipment can be required in order to avoid the risk of a spark that has enough energy to cause an ignition of the explosive atmosphere. This program provides calculations for the secondary explosion protection, especially for the installed measurements. Therefore it is according to the rules required to install intrinsic safe circuits. These circuits consist of a transformer, a cable and a sensor. These compounds have to fit to each other, properly. The program provides the corresponding calculations that are required to evaluate if the circuit is intrinsic safe or not. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
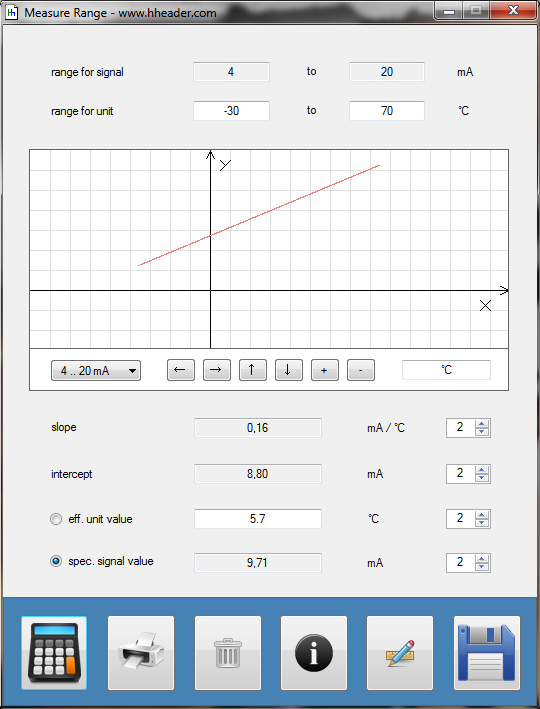
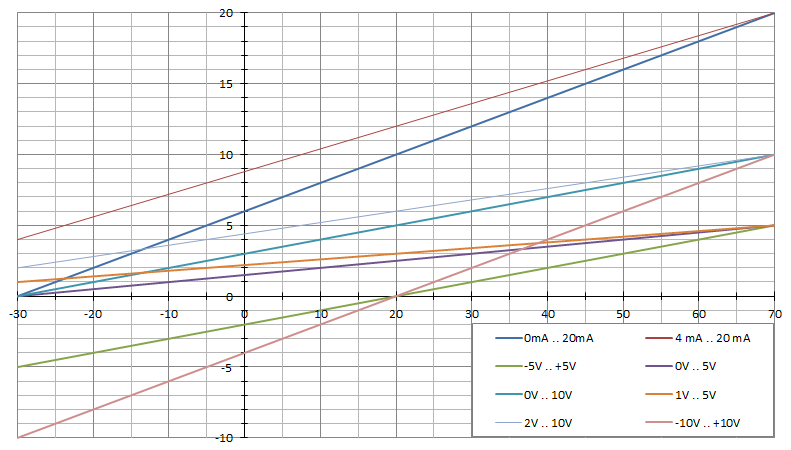
Category 5 - Electrics: Measure RangeFully or even partly automated plants nowadays have generally different sensors for measuring and control purposes. Thereby a physical value is measured with help of an electrical sensor and a corresponding signal transmitter. Principally the physical value is converted into an electrical signal by the sensor. The transmitter again converts the sensor signal into a linear standard signal that can be handled by a programmable logic controller. The program provides calculations for the corresponding conversions of a physical value into one of the usual standard signals. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
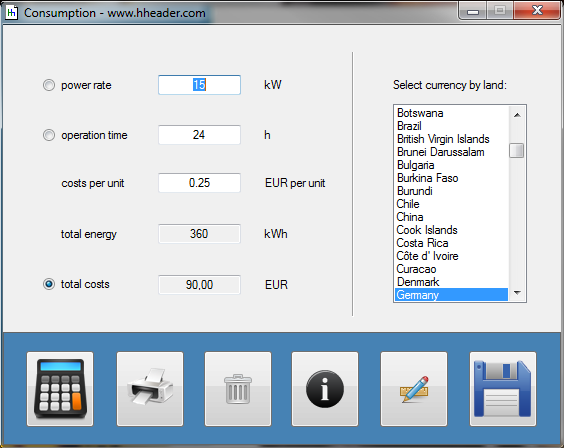
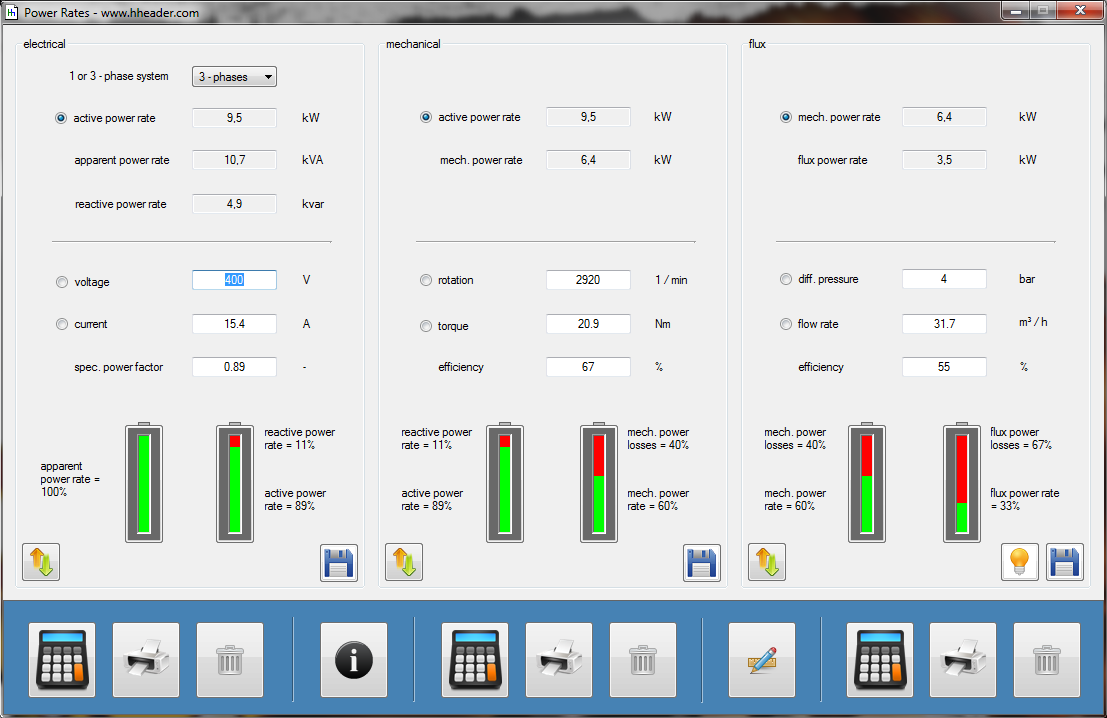
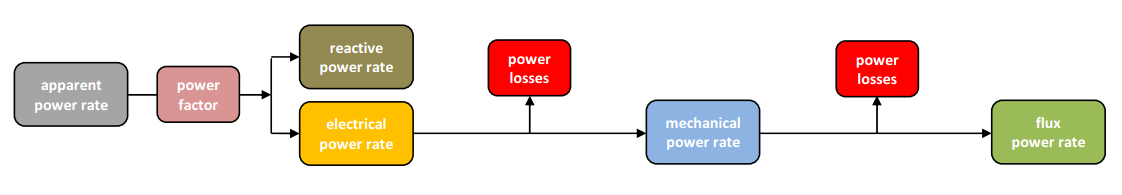
Category 5 - Electrics: Power RatesEnergy cannot get lost - energy can be converted from one kind to another kind. There are many different kinds of energy. Energy can appear, can be stored and can be converted. The law of conservation of energy is a powerful tool to evaluate technical or process circumstances. The program provides calculation for the operation of a pump, a fan or a blower, where at least the electrical supply power rate is divided up in the first, then converted into a mechanical power rate at the shaft of the stator and finally occurs as a power rate of a moving fluid at a certain pressure. Therefore the losses of power rate have to be considered as the efficiencies of the single stages. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
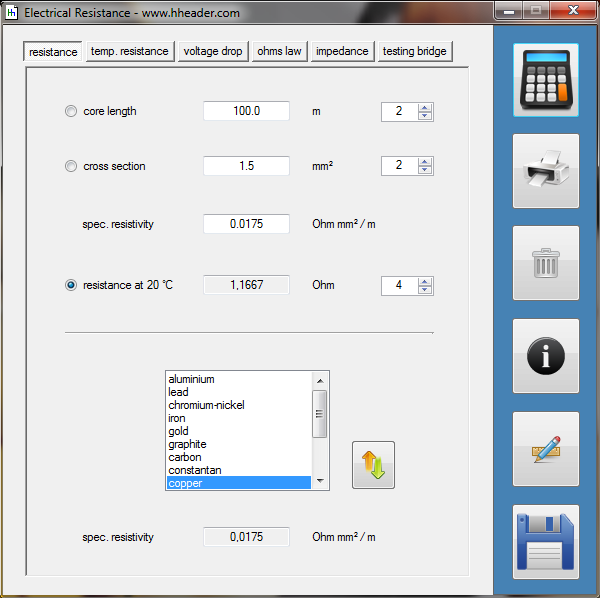
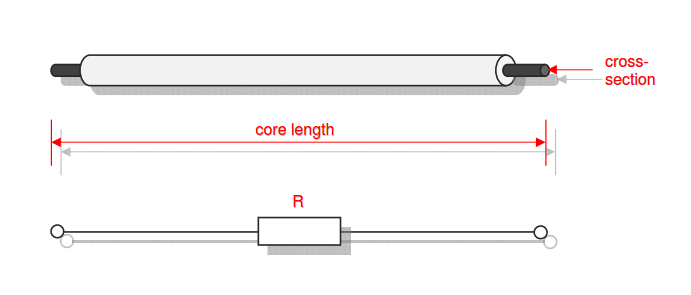
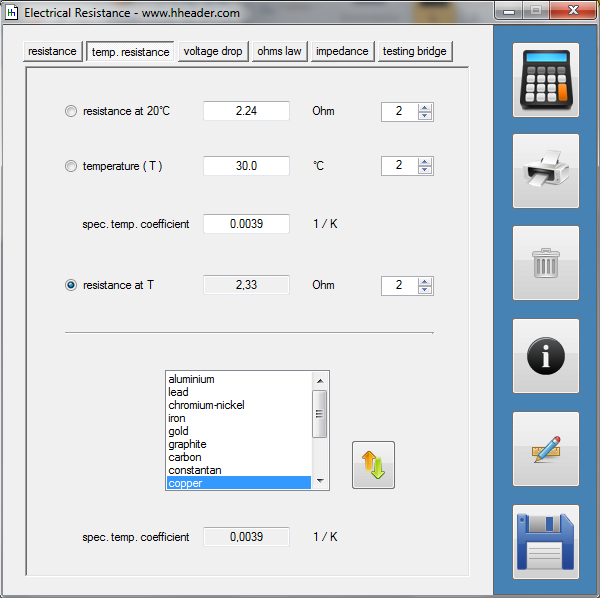
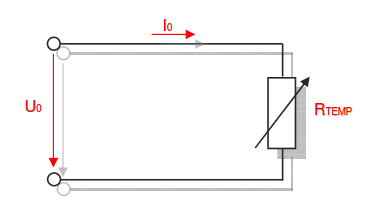
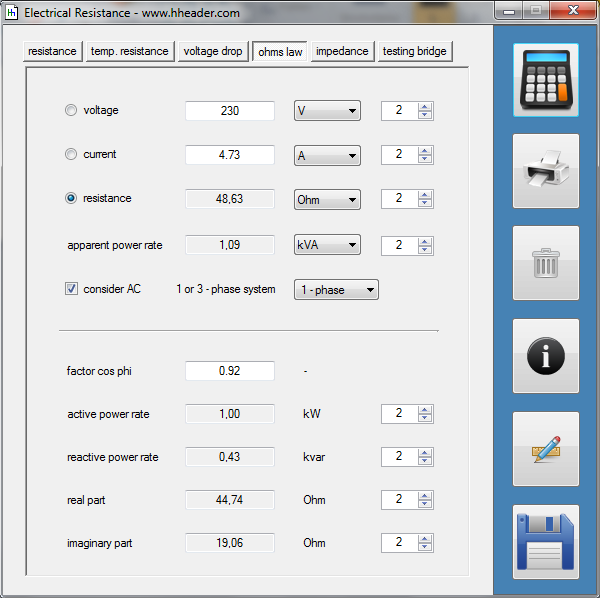
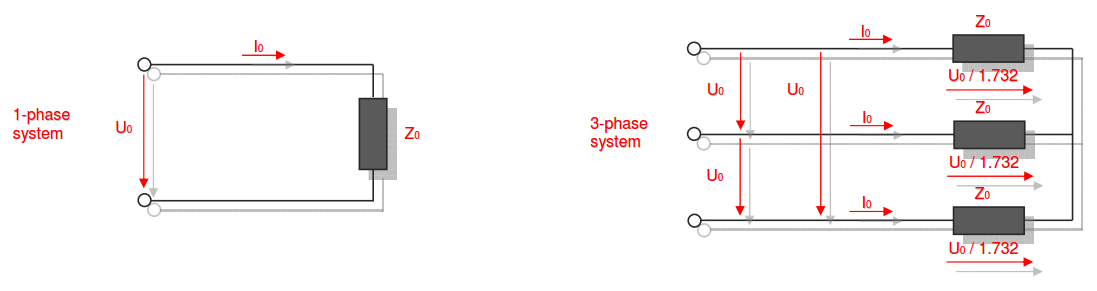
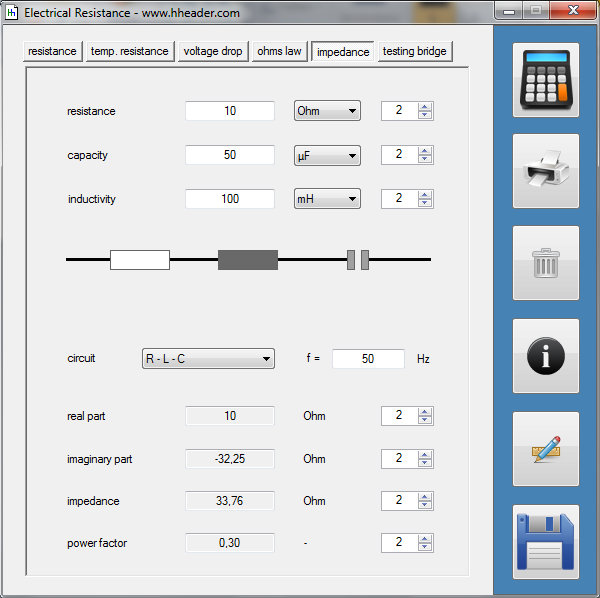
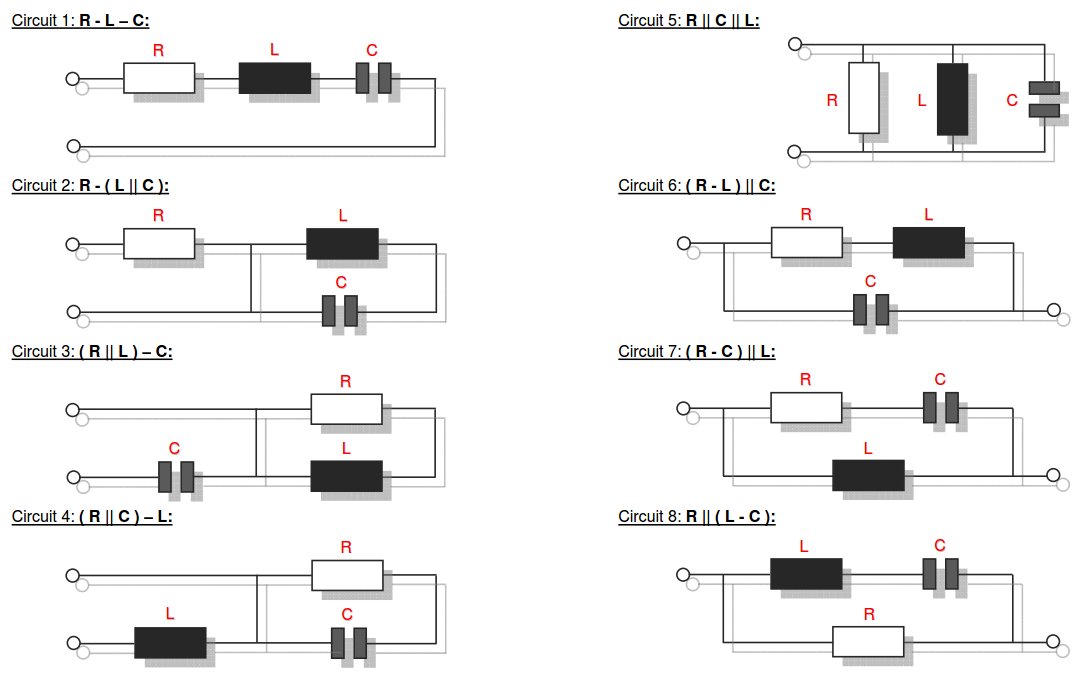
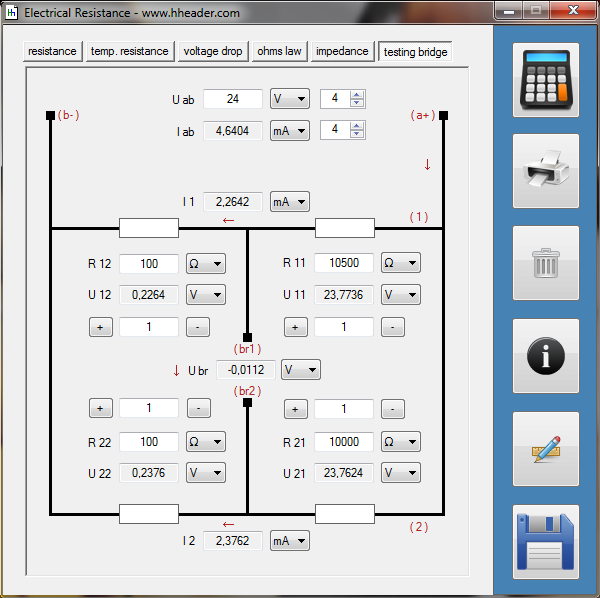
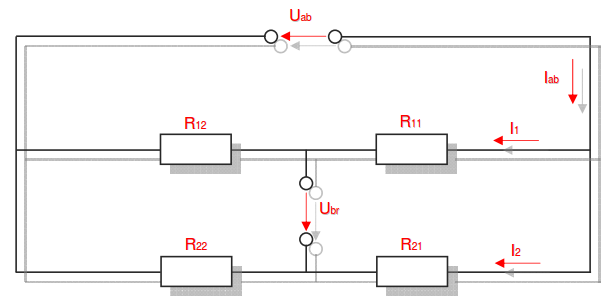
Category 5 - Electrics: Electrical ResistanceThe electrical resistance is not only in theory but also on site an important value. Resistance calculations can be used to check, if a cable is still in a proper condition or not, for example. The program provides six different subsections that are significant for practical evaluations in order to get a feeling for the supposable values and the practical circumstances. Calculations for the following subjects are provided: electrical resistance, temperature influences, voltage drop, ohms law, impedance, testing bridge. Especially the effects beside the supply with alternating current systems (AC) has to be taken into consideration on site. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|